Gantry Crane#
- Tags
Low damping, Tracking
- Available
1
- Inputs
2
- Outputs
3
Introduction#
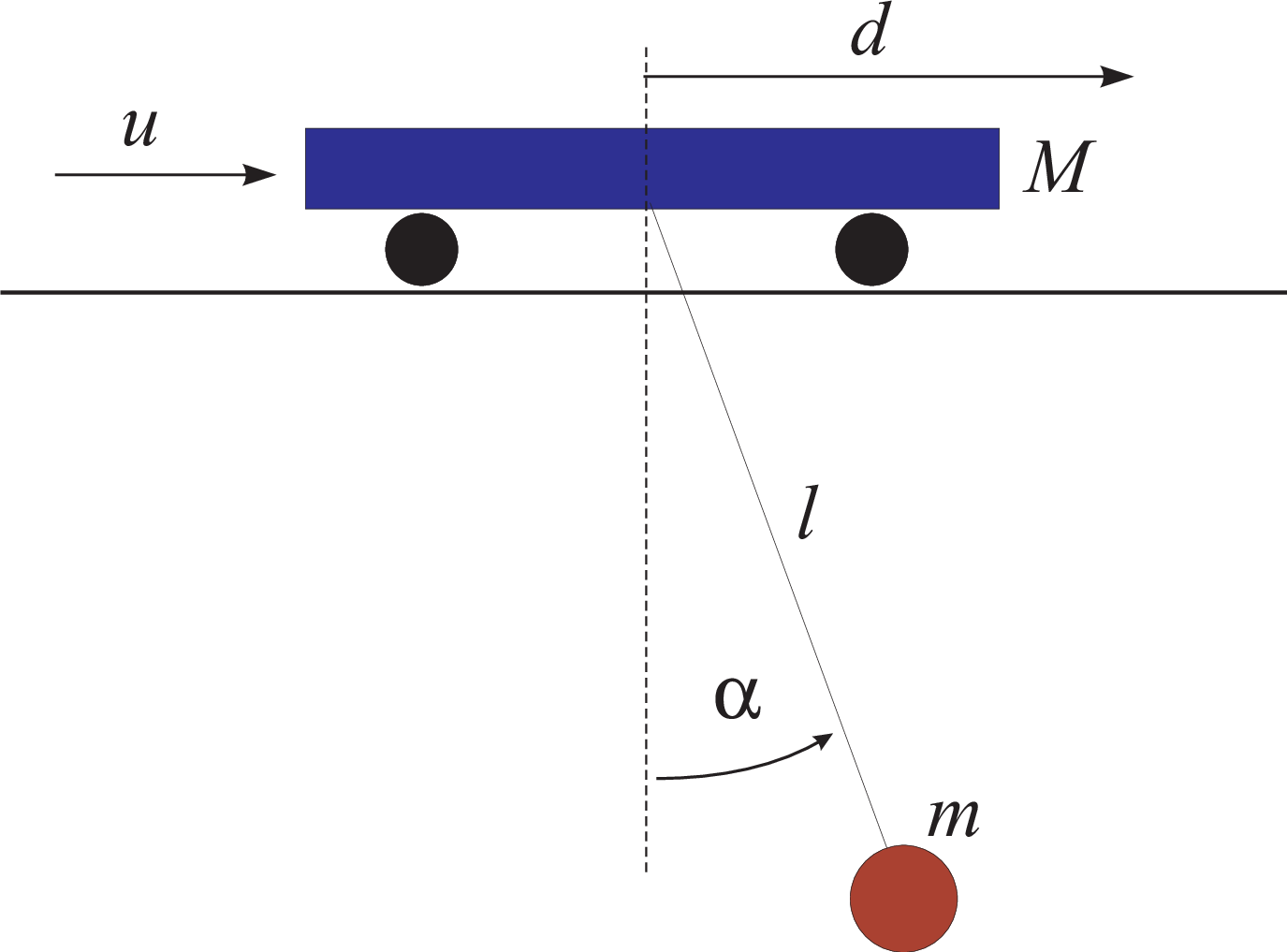
A trolley with mass \(M\) is driven by a DC motor with input \(u\) such that it travels in the lateral direction on a rail. The trolley carries a container of mass \(m\). The container is attached to the trolley by a cable of variable length \(l\). A second DC motor drives the hoist system.
|
|---|
Gantry crane setup. |
In the most basic form we only actuate the DC motor that drives the trolley, keeping the cable length constant. Then this system has one control input \(u\), which is the current that runs trough the DC motor. The system has an internal control loop that actively regulates this current. This input \(u\) is commanded from the computer and is scaled between -1 and +1. There are three measured outputs: \(d\) – the position of the trolley, \(\alpha\) – the angle between the cable and the vertical and \(l\) – the cable length.
Control Objective#
Design an anti-sway controller. The controlled system should be able to quickly follow a reference for the trolley position (given by the joystick or using a predefined signal), while minimizing the container swing. You can start with a constant cable length and, if time permits, design also a controller for the cable length.
Simulink Template#
A Simulink template cranetemplate.slx contains the necessary real-time interface blocks and some scopes. Make your own copy of this file and use it as a starting point for your experiments. Before starting the first simulation, define the sampling period \(h\) as a variable in the workspace of Matlab.