Tower crane#
- Tags
Low damping, Rotational, Tracking
- Available
1
- Inputs
3
- Outputs
3
Introduction#
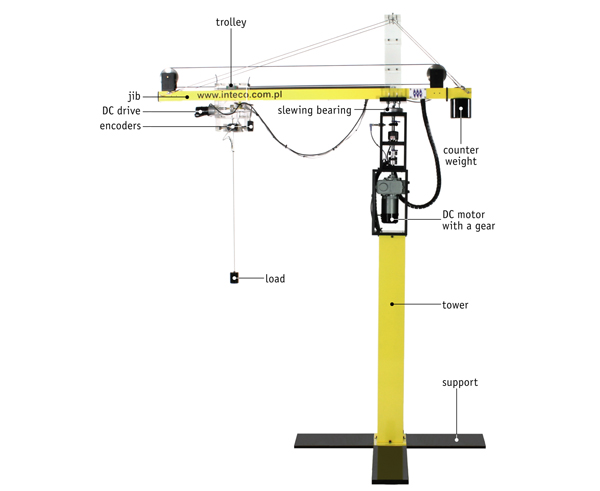
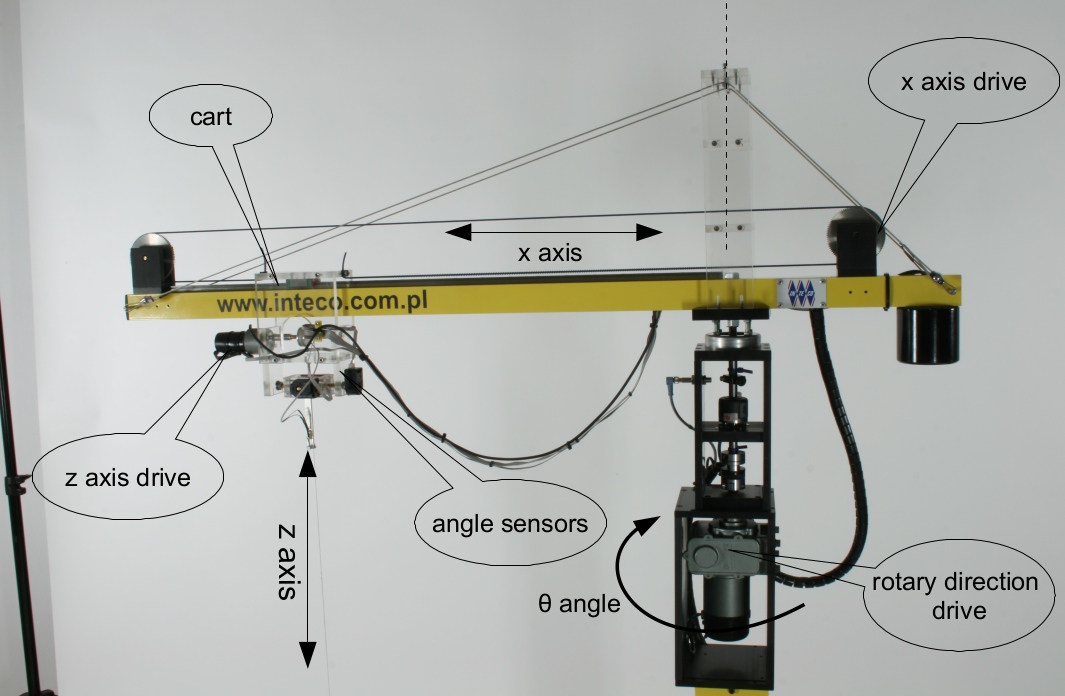
A trolley is driven via two motors on the horizontal plane (one linear axis and one rotation). A mass is attached to the trolley by a cable of variable length. A third motor drives the hoist system.
|
|---|
Tower crane setup. |
|
|---|
Tower crane setup. |
This system has three control inputs, one for the \(x\), \(\theta\), and \(z\) motor, each. This is a PWM signal corresponding to the velocity. There are five measured outputs: the \(x\), \(\theta\), and \(z\) position of the trolley as well as the \(x\) and \(y\) angle (local frame) that measure the sway. You may need to calibrate those measurements to correspond to their physical units, e.g., meters and radians.
Control Objective#
Design an anti-sway controller. The controlled system should be able to quickly follow a reference for the trolley position, while minimizing the mass swing. You can start with a constant cable length and only using the \(x\) axis. If time permits, design also a controller that additionally includes the cable length or the \(\theta\) axis.
Simulink Template#
A Simulink template contains the necessary real-time interface blocks and some scopes. Make your own copy of this file and use it as a starting point for your experiments. Before starting the first simulation, define the sampling period \(h\) as a variable in the workspace of Matlab.